What Is A Test Statistic
T-Test Significant
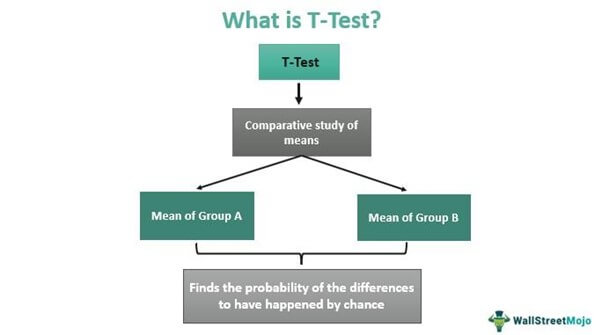
A T-test is the final statistical measure for determining differences between two means that may or may non be related. The testing uses randomly selected samples from the two categories or groups. It is a statistical method in which samples are called randomly, and there is no perfect normal distribution.
Y'all are free to employ this epitome on your website, templates, etc, Delight provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: T-Test (wallstreetmojo.com)
The blazon of T-exam to exist conducted is decided by whether the samples to be analyzed are from the same category or distinct categories. The inference obtained in the procedure indicates the probability of the mean differences to accept happened by chance. The test is useful when comparing population historic period, length of crops from two different species, student grades, etc.
Table of contents
- T-Test Meaning
- T-Test Explained
- Assumptions
- Types
- #1 – One-Sample T-Exam
- #2 – Independent Two-Sample T-Test
- #3 – Paired Sample T-Test
- #4 – Equal Variance T-Test
- #five – Unequal Variance T-Examination
- Example With Calculation
- Ofttimes Ask Questions (FAQs)
- Recommended Articles
- A T-test is a statistical method of comparing the means or proportions of ii samples gathered from either the aforementioned group or different categories.
- It is aimed at hypothesis testing, which is used to test a hypothesis pertaining to a given population.
- It is the difference between population means and a hypothesized value.
- Ane-sample, two-sample, paired, equal, and unequal variance are the types of T-tests users can use for hateful comparisons.
T-Examination Explained
A T-examination studies a prepare of data gathered from 2 similar or dissimilar groups to determine the probability of the difference in the result than what is unremarkably obtained. The accuracy of the exam depends on various factors, including the distribution patterns used and the variants influencing the collected samples. Depending on the parameters, the test is conducted, and a T-value is obtained as the statistical inference of the probability of the usual resultant being driven by chance.
For example, if one wishes to figure out if the hateful of the length of petals of a flower belonging to two different species is the aforementioned, a T-test can be done. The user can select petals randomly from two other species of that flower and come to a standard conclusion. The finalT-examination interpretation could be obtained in either of the 2 ways:
- A null hypothesis Nothing hypothesis presumes that the sampled information and the population information have no divergence or in simple words, it presumes that the merits made past the person on the data or population is the accented truth and is always right. Then, even if a sample is taken from the population, the result received from the study of the sample will come up the same equally the assumption. read more signifies that the difference between the means is nil and where both the means are shown as equal.
- An alternate hypothesis implies the difference betwixt the means is unlike from cypher. This hypothesis rejects the null hypothesis, indicating that the data prepare is quite accurate and not by chance.
This T-test, still, is just valid and should be done when the mean or average of but two categories or groups needs to exist compared. Equally shortly as the number of comparisons to be made is more than ii, conducting this is non recommended.
Assumptions
The examination runs on a set of assumptions, which are as follows:
- The measurement calibration used for such hypothesis testing Hypothesis Testing is the statistical tool that helps mensurate the probability of the correctness of the hypothesis effect derived later performing the hypothesis on the sample data. It confirms whether the chief hypothesis results derived were right. read more follows a set of continuous or ordinal patterns. The accounted parameters and variants influencing the samples and surrounding the groups are based on the standard consideration.
- The tests are completely based on random sampling. As no individuality is maintained in the samples, the reliability is frequently questioned.
- When the information is plotted with respect to the T-test distribution, it should follow a normal distribution Normal Distribution is a bell-shaped frequency distribution bend which helps describe all the possible values a random variable can accept within a given range with near of the distribution surface area is in the middle and few are in the tails, at the extremes. This distribution has ii key parameters: the mean (µ) and the standard deviation (σ) which plays a key part in assets return adding and in hazard direction strategy. read more and bring nigh a bell-curved graph.
- For a clearer bell curve Bell Bend graph portrays a normal distribution which is a type of continuous probability. It gets its name from the shape of the graph which resembles to a bell. read more than , the sample size The sample size formula depicts the relevant population range on which an experiment or survey is conducted. It is measured using the population size, the critical value of normal distribution at the required confidence level, sample proportion and margin of fault. read more than needs to be bigger.
- The variance should be such that the standard deviations Standard deviation (SD) is a popular statistical tool represented by the Greek letter 'σ' to measure the variation or dispersion of a ready of data values relative to its mean (average), thus interpreting the information's reliability. read more of the samples are almost equal.
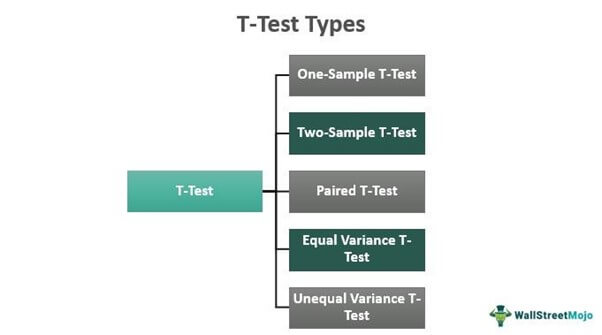
Types
Some of the widely usedT-exam types are every bit follows:
You are complimentary to utilise this epitome on your website, templates, etc, Please provide u.s. with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: T-Exam (wallstreetmojo.com)
#1 – 1-Sample T-Test
While performing this exam, the hateful or boilerplate of one group is compared against the set average, which is either the theoretical value or means of the population. For instance, a teacher wishes to figure out the average height of the students of class 5 and compare the aforementioned against a prepare value of more than 45 kgs.
The teacher first randomly selects a group of students and records private weights to achieve this. Next, she finds out the mean weight for that group and checks if it meets the standard fix value of 45+. The formula used to obtain one-sample t-exam results is:
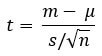
Where,
- T = t-statistic
- m = mean of the group
- = theoretical mean value of the population
- south = standard deviation of the group
- n = sample size
#2 – Independent Ii-Sample T-Test
This is the test conducted when samples from ii different groups, species, or populations are studied and compared. It is likewise known as an independent T-examination. For case, if a teacher wants to compare the height of male students and female students in class five, she would utilize the contained 2-sample test.
TheT-exam formula used to calculate this is:
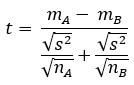
Where,
- mA – mB = means of samples from 2 different groups or populations
- nA – nB = corresponding sample sizes
- s2 = standard departure or common variance of ii samples
#3 – Paired Sample T-Test
This hypothesis testing is conducted when two groups belong to the same population or group. The groups are studied either at two different times or under two varied conditions. The formula used to obtain the t-value is:
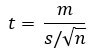
Where,
- T = t-statistic
- m = hateful of the group
- = theoretical mean value of the population
- due south = standard deviation of the grouping
- due north = sample size
#4 – Equal Variance T-Test
This examination is conducted when the sample size in each grouping or population is the same or the variance of the two data sets is similar. It is also referred to every bit pooled T-test. The formula practical here is as follows:
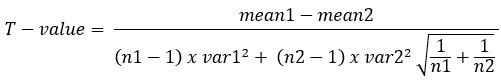
Where,
- Mean1 and mean2 = average value of each set of samples
- var1 and var2 = variance of each prepare of samples
- n1 and n2 = number of records in each set up
#five – Unequal Variance T-Test
The diff variance testing is used when the variance and the number of samples in each group are unlike. Information technology is oftentimes referred to as Welch's examination, and the formula is:
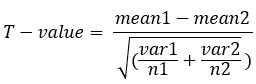
Where,
- mean1 and mean2 = Average value of each prepare of samples
- var1 and var2 = Variance of each set of samples
- n1 and n2 = number of records in each set
Instance With Calculation
Permit u.s. consider the scores for each subject in the test held in two phases.
| Subject area | Marks Phase i | Marks Stage two |
| Maths | 45 | 62 |
| Physics | 45 | 55 |
| Chemistry | 45 | 55 |
| Biological science | fifty | 65 |
| History | 55 | 68 |
| Geography | fourscore | lxx |
Footstep i: Subtract the marks scored in both the phases
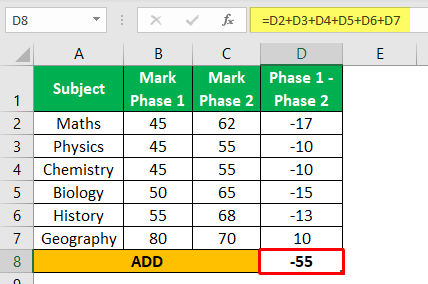
Step 2: Add up all the differences, i.e., -55
Step 3: Foursquare up the differences
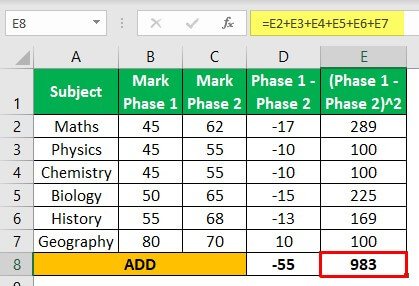
Step 4: Add up all the squares of departure, i.e., 983
Step five: Usage of formula to summate the T value
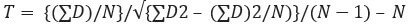
- =-9.16/√ {983-(-55)2/6)}/ (half-dozen-i) *half dozen
- = -nine.16/√15.96
- =-9.16/3.99
T Value = -ii.29
Now, go the degrees of freedom Degrees of liberty (df) refers to the number of contained values (variable) in a data sample used to find the missing piece of information (fixed) without violating any constraints imposed in a dynamic organisation. These nominal values have the freedom to vary, making information technology easier for users to detect the unknown or missing value in a dataset. read more than . To obtain this, subtract 1 from the sample size (six – 1 =five). The next affair is to notice out the p-value P-Value, or Probability Value, is the deciding gene on the null hypothesis for the probability of an assumed result to exist true, being accustomed or rejected, & acceptance of an alternative issue in case of the assumed results rejection. read more , which, if smaller in value, supports the zip hypothesis result. For case, if the p-value is something around 0.9, i.e., xc%, it indicates that the T-value obtained has the probability of beingness a random observation. On the other hand, if the p-value is around 0.025, i.e., 2.v%, the result or t-value obtained is significant.
Frequently Enquire Questions (FAQs)
What is a T-Test?
T-examination measures the difference between two ways, which may or may not be related to each other, indicating the probability of the differences to take happened by chance. The accuracy of the values obtained depends on various factors, including the distribution patterns used and the variants influencing the nerveless samples.
When is the T-Examination used?
A T-Test is only valid and should be done when ways of only two categories or groups need to be compared. Every bit before long as the number of comparisons to be made is more ii, conducting this exam is not recommended.
• One-sample is used to observe out the hateful or average of ane group to compare information technology against the set average.
• An independent Ii-Sample exam is conducted when samples from two different groups, species, or populations are studied and compared.
• Paired Sample is the hypothesis testing conducted when ii groups belong to the same population or group.
• Equal Variance is conducted when the sample size in each group or population is the aforementioned, or the variance of the ii data sets is similar.
• Unequal Variance is used when the variance and the number of samples in each group are different.
What are T-Tests and P values?
While the T values signal the chances of the departure between the sample means being a result obtained past chance, p-values reverberate the probability of having sufficient proof to negate the indifference between the mean of the two samples.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is T-Test & its Meaning. Hither we explain how T-Test works along with its formula, adding, types, assumptions, and examples. You can learn more about from the following articles –
- Z Exam in Excel
- Formula of P Value
- Statistics in Excel
- Formula of F-Test
What Is A Test Statistic,
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/t-test/
Posted by: robertscoge1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Test Statistic"
Post a Comment